electron withdrawing groups|Radicals as Exceptional Electron : Cebu An electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effects. Electron-withdrawing groups have significant impacts on . Tingnan ang higit pa Jackpots and Progressive Jackpots - the Highest Paying Slot Machines. . Let’s say the lowest payout of a slot (Slot A) could be 0.5 times the bet. The average payout could be 5 times the bet. The highest one could be 20 times the total bet. Yet, another slot (Slot B) with the same RTP value and volatility can have a better paytable. .
PH0 · Recent Progress of
PH1 · Radicals as Exceptional Electron
PH2 · Radically new reactivity
PH3 · More EAS
PH4 · Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups
PH5 · Electron
PH6 · Activating and Deactivating Groups In Electrophilic
PH7 · 7.10: Carbocation Structure and Stability
PH8 · 20.4 Substituent Effects on Acidity
Follow @kpopfap for the hottest and sexiest photos and videos of your favorite K-pop idols. Warning: NSFW content. #fap
electron withdrawing groups*******An electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effects. Electron-withdrawing groups have significant impacts on . Tingnan ang higit paEffects on Bronsted acidityElectron-withdrawing groups exert an "inductive" or "electron-pulling" effect on covalent . Tingnan ang higit paRadicals as Exceptional Electron• Electron-donating group Tingnan ang higit pa
Electron-withdrawing groups are the opposite effect of electron-donating groups (EDGs). Both describe functional groups, however, electron-withdrawing groups pull electron . Tingnan ang higit pa
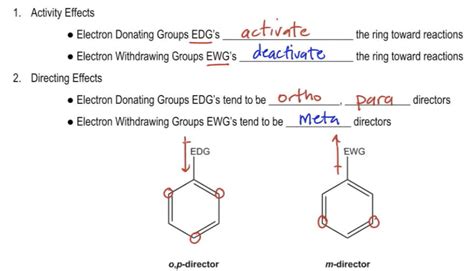
The more electron-rich the aromatic ring, the faster the reaction. Groups that can donate electron density to the ring make EAS reactions faster. If a substituent increases the rate of reaction relative to .electron withdrawing groups Radicals as Exceptional Electron Learn how electron donating and withdrawing groups affect the position of additional substituents on a benzene ring during .
Well, things get a little more complicated. In this episode of Crash Course Organic Chemistry, we’ll continue our exploration of EAS reactions by looking at electron donating groups and.
Learn how carbocations are stabilized by alkyl groups through inductive effects and hyperconjugation. Electron-withdrawing groups destabilize carbocations by reducing the electron density on the carbocation carbon.
Learn how electron-withdrawing and electron-releasing groups affect the acidity of carboxylic acids and benzoic acids. See examples, diagrams, and explanations of inductive and resonance effects. Additional mechanistic and computational studies indicate that the key phenoxyl intermediate serves as an open-shell electron-withdrawing group in these reactions, lowering the barrier for . Fluorophenols can be activated towards SNAr reactions by forming a transient electron-withdrawing phenoxyl radical.Electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) have emerged as a powerful tool for the activation of various arenes to promote nucleophilic dearomative additions for the construction of complicated chiral cyclic structures .In organic chemistry, electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) and electron donating groups (EDGs) play a crucial role in determining molecular reactivity. These effects influence .Just as electron-donating groups can stabilize a carbocation, electron-withdrawing groups act to destabilize carbocations. Carbonyl groups are electron-withdrawing by inductive effects, due to the polarity of the .
Electron withdrawing group (EWG): An atom or group that draws electron density from neighboring atoms towards itself, usually by resonance or inductive effects. Trifluoro acetate ion is a weaker base than acetate ion because the trifluoromethyl group is attracting electron density away from the carboxylate .Hydroxyl, alkoxyl, and amino groups have a weaker electron-withdrawing inductive effect but a stronger electron-donating resonance effect and are thus activators. All are ortho and para directors, however, because of the lone pair of electrons on the atom bonded to .
Electron withdrawing groups (EWG) have very much affinity towards electrons. When such a group is present in a molecule then most of the charge density will be partially shifted towards EWG. Eg. In nitromethane , EWG present is present and it is Nitro group(NO2) . In this molecule NO2 has partial negative charge since it attracts the .
If the most common type of coupling partner contains electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs), the radical is considered nucleophilic, whereas if the most common partner possesses electron-donating .Fluoroacetate anion stabilized by electron withdrawing inductive effect of fluorine. A similar effect is seen when other electron-withdrawing groups are attached to -CH 2 CO 2 H. As the power of the electron-withdrawing group becomes stronger there is a corresponding drop in the pK a of the carboxylic acid. In the previous episode we discussed what happens when we use electrophilic aromatic substitution to add a group to a benzene ring, but what happens when you.Electron with-drawing groups can decrease the electron density at the nucleus, deshielding the nucleus and result in a larger chemical shift. Compare the data in the table below. . The effects are cumulative so the presence of more electron withdrawing groups will produce a greater deshielding and therefore a larger chemical shift, i.e .

The nitro group (-NO 2), and the positively charged, tetra-substituted amino group (consider the structure once this trimethyl amino group is connected to the aryl ring) are both electron-withdrawing. As the trimethyl amino group will have an overall positive charge (and the nitro group is neutral overall), the trimethyl amino group is the .electron withdrawing groupsIn Organic chemistry, the inductive effect in a molecule is a local change in the electron density due to electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups elsewhere in the molecule, resulting in a permanent dipole in a bond. [1] It is present in a σ (sigma) bond, unlike the electromeric effect which is present in a π (pi) bond.. The halogen atoms in an .
except-R, -Ar or -vinyl (hyperconjugation, π electrons) EWG = electron withdrawing group; EWG can be recognised either by the atom adjacent to the π system having several bonds to more electronegative atoms, . The placement of electron withdrawing groups ortho-or para-to the leaving group results in faster reactions than does the placement of electron withdrawing groups meta-to the leaving group .Electron withdrawing group (EWG): An atom or group that draws electron density from neighboring atoms towards itself, usually by resonance or inductive effects. Trifluoro acetate ion is a weaker base than acetate ion because the trifluoromethyl group is attracting electron density away from the carboxylate . The presence of an electron-withdrawing group - such as a fluorine atom - will significantly destabilize a carbocation through the inductive effect. Carbonyl groups are electron-withdrawing by inductive effects, due to the polarity of the \(C=O\) double bond. It is possible to demonstrate in the laboratory (we'll see how in problem 14.x) that . The electron-withdrawing group causes the energy level associated with the singly occupied molecular orbital of the substituted radical to move to a position lower in energy; that is, the radical becomes more stable. 6,32 When the energy level of an SOMO in a carbon-centered radical becomes sufficiently low, the major, frontier .Aromatic amines. Aromatic amines have the nitrogen atom directly connected to an aromatic ring structure. Due to its electron withdrawing properties, the aromatic ring greatly decreases the basicity of the amine – and this effect can be either strengthened or offset depending on what substituents are on the ring and on the nitrogen. The presence .
Electron withdrawing group (EWG): An atom or group that draws electron density from neighboring atoms towards itself, usually by resonance or inductive effects. Trifluoro acetate ion is a weaker base than acetate ion because the trifluoromethyl group is attracting electron density away from the carboxylate .
For p-Nitroaniline virtually all of the electron density, shown as a red/yellow color. is pulled toward the electron-withdrawing nitro group. In p-methoxyaninline the electron donating methoxy group donates electron density into the ring. The amine in p-methoxyaniline is shown to have more electron density, shown as a yellow color, when .
The official site of the National Basketball Association. Follow the action on NBA scores, schedules, stats, news, Team and Player news.
electron withdrawing groups|Radicals as Exceptional Electron